Conclusions #
Expanding the Applications of Shaders beyond 3D Graphics #
While shaders are commonly associated with 3D graphics, their applications are not limited to this domain. Shaders can also be used in 2D graphics to achieve interesting and visually appealing effects. For example, in 2D games or image processing applications, shaders can be employed for tasks such as color blending or creating photo mosaics.
Enhancing Visual Realism through Shaders #
Shaders have proven to be a powerful tool for enhancing the visual quality and realism of computer-generated images. Through their programmability, shaders enable the simulation of complex lighting models and material properties, resulting in realistic effects such as dynamic shadows, reflections, refractions, and global illumination. This level of realism greatly enhances the immersion and visual appeal of computer-generated graphics.
Challenges in Shader Development #
Shader development presents various challenges that need to be overcome. One significant difficulty is optimizing shader code to achieve real-time performance. Balancing visual quality and rendering speed requires careful consideration of algorithmic efficiency and hardware limitations. Additionally, the learning curve associated with shader programming can discourage some developers from fully exploring its potential. Providing accessible resources, tutorials, and tools can help overcome this barrier and encourage wider adoption of shaders in visual computing.
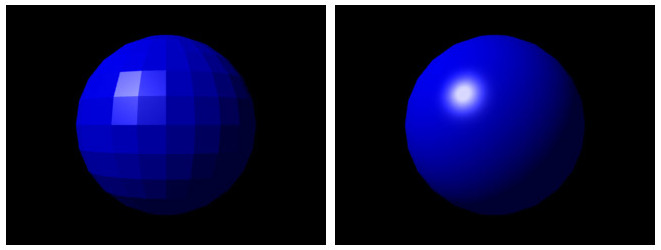
Future Work #
Advancements in Lighting Models and Material Representations #
Continued research and implementation of advanced lighting models and material representations can lead to even more realistic and accurate visual effects. Exploring physically-based rendering techniques enables the creation of shaders that closely mimic real-world lighting and material interactions, resulting in highly convincing visuals.
Performance Optimization and Hardware Acceleration #
Further optimization of shader performance is crucial to expand its applications in resource-constrained environments. Leveraging parallel computing techniques and hardware acceleration can unlock the potential of shaders in scenarios such as mobile devices or virtual reality systems. Finding innovative ways to maximize computational efficiency and leverage hardware capabilities will be essential for pushing the boundaries of real-time rendering with shaders.