Intro & Background #
Visual Illusions #
Visual illusions are phenomena that make us perceive something that is not present or that distorts our perception of reality. These illusions are produced by the complex interaction between our visual system and our brain.
The brain receives information through the eyes and processes it to create a coherent image of the world around us. However, this process is not always perfect and can be fooled by various visual illusions that make us perceive things differently than they really are.
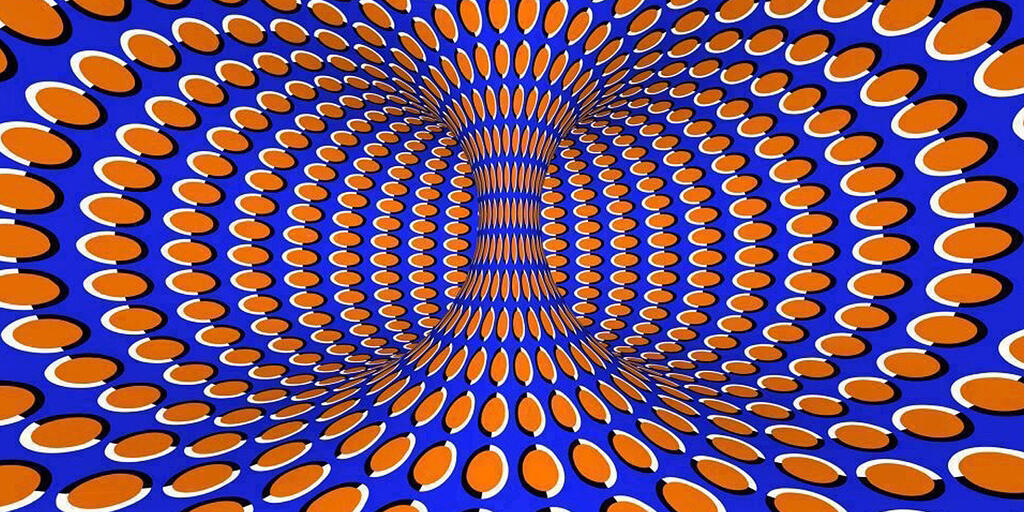
These illusions can be produced in many ways, from the manipulation of light and color to the manipulation of shape and perspective. Some visual illusions are quite simple and can be easily produced, while others are much more complex and require a deeper understanding of neuroscience and psychology.
Visual illusions have a wide range of practical applications in a variety of fields. From advertising and entertainment, to medicine and architecture, being a useful tool to create interesting visual effects and to better understand how our visual perception and brain works.
Color Blindness #
However, not all living beings see the world in the same way, either because we have different interpretations of reality or because physiologically there are differences that limit or alter the ability to perceive the environment with which we visually interact. This is the case of color blindness.
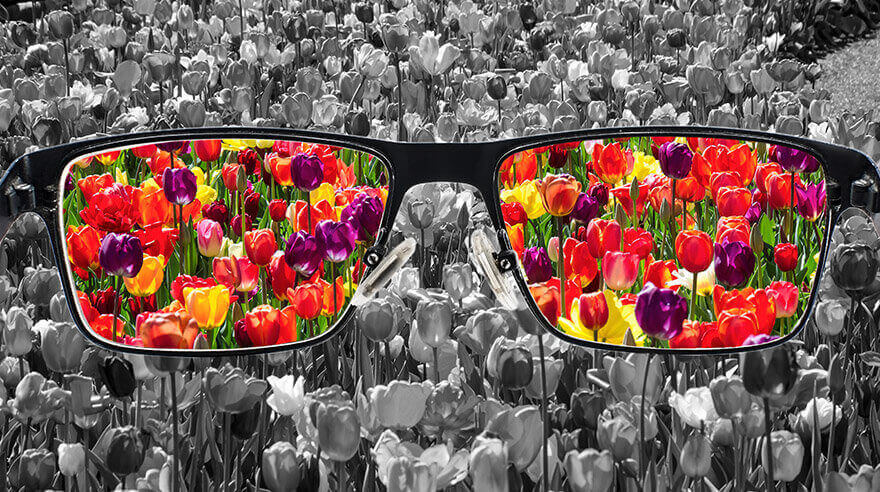

Color blindness is a vision disorder that affects the ability to distinguish certain colors. This disorder mainly affects men, since it is transmitted through the X chromosome and men only have one X chromosome, while women have two. It is said to affect 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women.
This disorder is caused by a defect in the retinal cones, the light-sensitive cells at the back of the eye. The cones are divided into three types, each sensitive to different wavelengths of light, corresponding to the colors red, green, and blue. In color blindness, one or more of these types of cones don’t work correctly, causing colors to look different or indistinguishable.

Types of Color Blindness #
There are multiple and different types of color blindness, depending on which type of cone is affected and to what extent:
First, there is red-green color blindness. This is the most common type of color blindness, making it difficult to distinguish between the color red and green. There are 4 types of red-green color blindness:
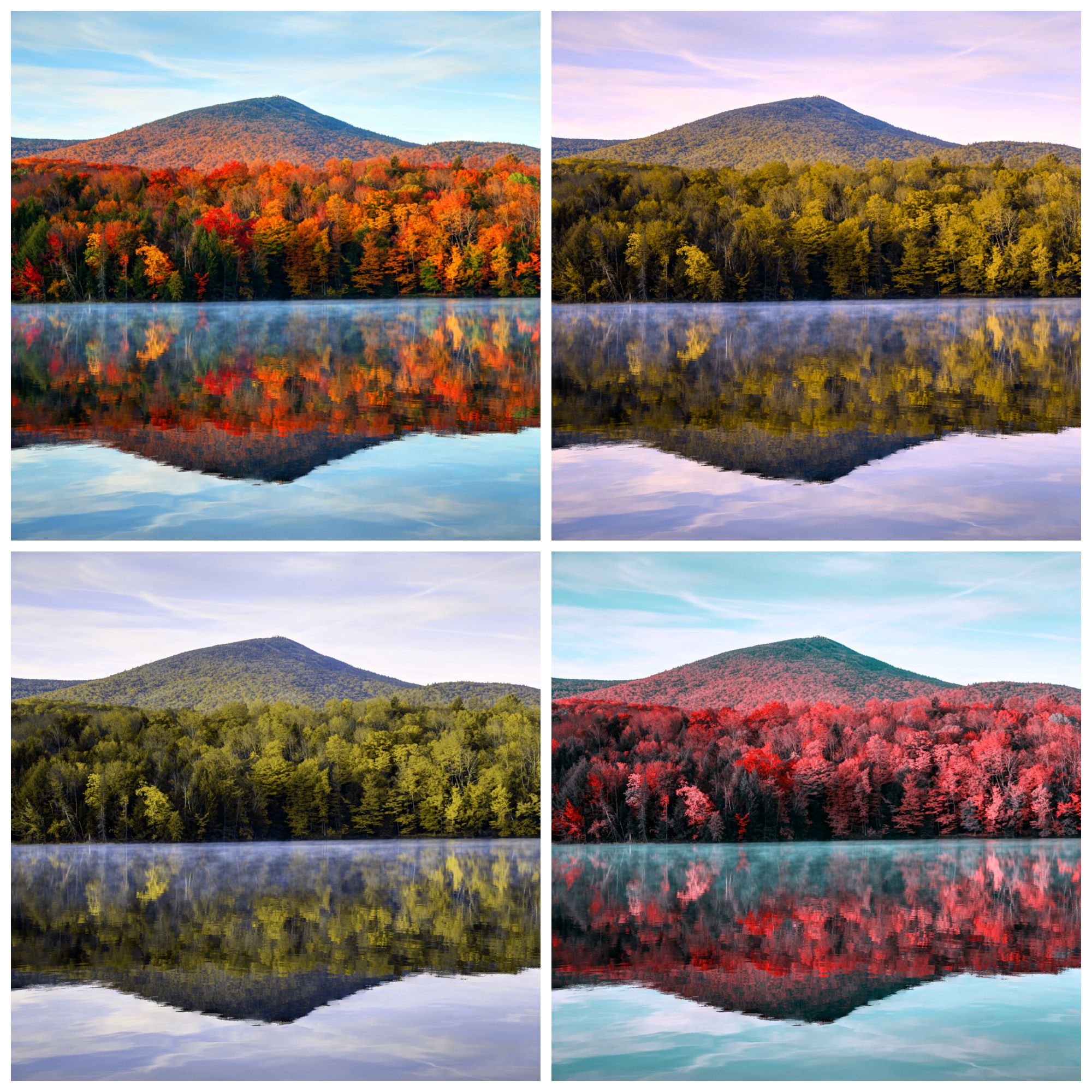
- Deuteranomaly: The most common type of red-green color blindness. Makes green look redder. This type is mild and usually does not interfere with normal activities.
- Protanomaly: makes red appear greener and less bright. This type is mild and usually does not interfere with normal activities.
- Protanopia and deuteranopia: both types cause you to be unable to tell the difference between red and green.
Then, there is blue-yellow color blindness. This less common type of color blindness makes it difficult to distinguish between the color blue and green, and between yellow and red.
There are 2 types of blue-yellow color blindness:
- Tritanomaly: makes it difficult to tell the difference between blue and green, and between yellow and red.
- Tritanopia: Causes you to be unable to distinguish between blue and green, purple and red, and yellow and pink. It also makes colors appear less bright.
And finally, complete color blindness. If you are completely color blind, you cannot see colors at all. This is also known as monochromacy and is very rare. Depending on the type, you may also have trouble seeing clearly and be more sensitive to light.
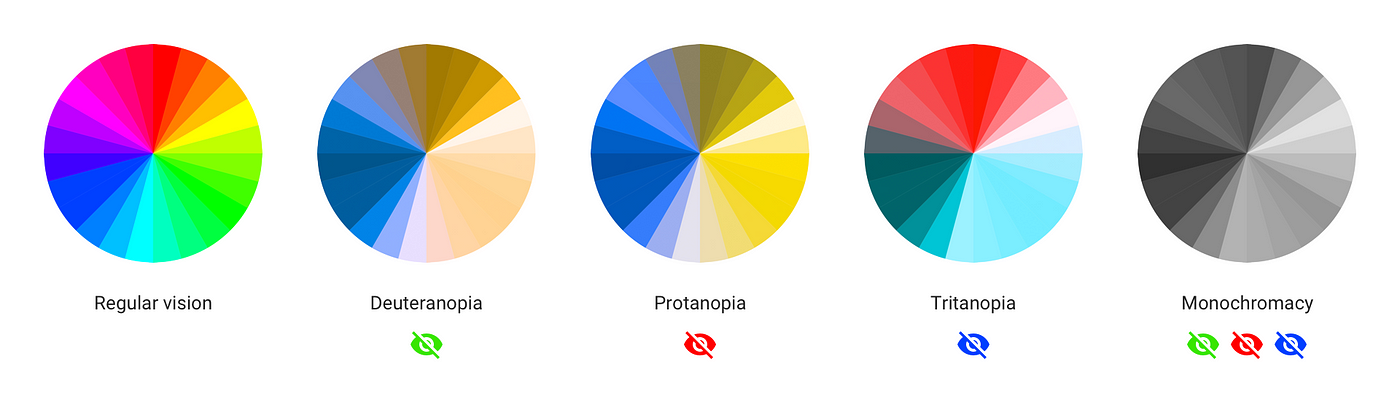
Color blindness can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, for example on activities such as driving or choosing clothing. However, there are tools and technologies available to help people with color blindness, such as color correction glasses and filters.
Visual illusions can also be used to study color blindness and color perception in general. For example, some visual illusions, such as the Ishihara images, are used to diagnose color blindness and determine which types of cones are affected. Visual illusions have also been used to study how the brain processes colors and how this can vary in people with color blindness.
Currently, color blindness is a key aspect to consider in the development of applications and websites that seek to be accessible and inclusive. Likewise, there are a variety of visual aid tools for people with this disorder, which allow them to see and interact with the world more comfortably, either physically or on the Internet.
Coloring #
Coloring in visual computing refers to the process of applying or modifying color information in digital images or videos. It involves techniques and algorithms that manipulate the color channels of an image to achieve various effects, enhance visual appearance, or convey specific information. Coloring can be used for tasks such as image enhancement, color correction, artistic rendering, and image manipulation. It plays a crucial role in computer graphics, computer vision, and image processing applications, enabling the generation of realistic and visually appealing images and videos.
Masking #
Masking in visual computing is a technique used to isolate or extract specific regions or objects of interest from an image or video. It involves creating a binary mask that defines the regions to be retained or discarded for further processing. A mask is typically a grayscale image, where the white pixels represent the areas of interest (foreground), and the black pixels represent the areas to be ignored (background). Masking is extensively used in computer vision tasks such as object recognition, segmentation, tracking, and image editing. By accurately defining the regions of interest, masking enables targeted analysis and manipulation of visual content, facilitating various computer vision applications.
In the present work, practical exercises related to visual illusions will be addressed, more specifically, focused on color blindness.